
- Home
- Products
- About Us
- Contact Us
More Information
(+98) 912 833 4643

(+98) 912 833 4643
*TEG (Triethylene Glycol)* is a chemical compound belonging to the glycol family, widely used in various industrial applications due to its hygroscopic and solvent properties.
*Properties of TEG:*
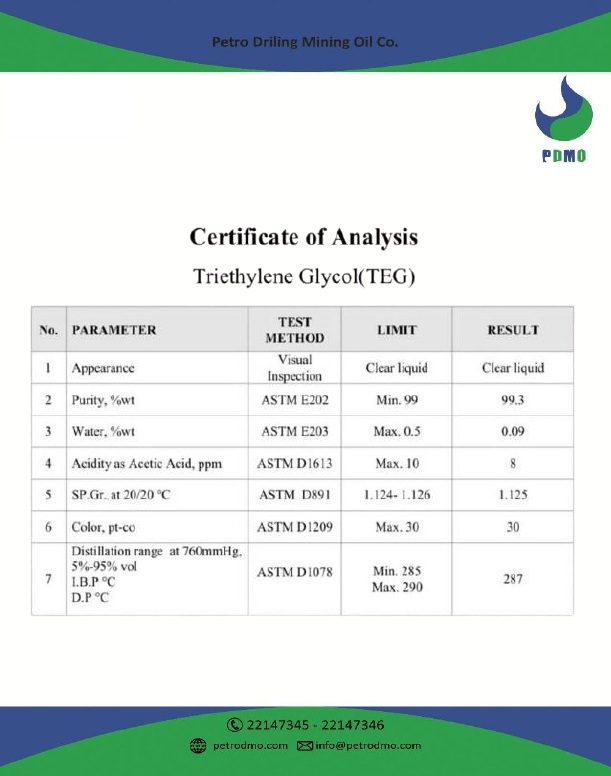
1. *Chemical Formula*: C₆H₁₄O₄
2. *Molecular Weight*: 150.17 g/mol
3. *Appearance*: Clear, colorless, and odorless liquid.
4. *Density*: 1.125 g/cm³ at 20°C.
5. *Boiling Point*: 285°C.
6. *Melting Point*: -7°C.
7. *Solubility*: Miscible with water, alcohols, and many organic solvents.
8. *Hygroscopic Nature*: Absorbs moisture from the air.
*Production Process of TEG:*
*TEG (Triethylene Glycol)* is a chemical compound belonging to the glycol family, widely used in various industrial applications due to its hygroscopic and solvent properties.
1. *Ethylene Oxide Production*:
– Ethylene (derived from petroleum or natural gas) is oxidized in the presence of a catalyst to produce ethylene oxide (EO).
2. *Hydration Reaction*:
– Ethylene oxide reacts with water to form MEG, DEG, and TEG. The reaction conditions (temperature, pressure, and catalyst) determine the ratio of these products.
3. *Separation and Purification*:
– The crude mixture of MEG, DEG, and TEG is separated through distillation. TEG is collected as a higher boiling fraction.
4. *Final Product*:
– The purified TEG is stored in tanks and transported for industrial use.
—
*Applications of TEG:*
1. *Gas Dehydration*:
– TEG is widely used in natural gas processing to remove water vapor from the gas stream, preventing hydrate formation and corrosion in pipelines.
2. *Solvents*:
– TEG is used as a solvent in paints, inks, resins, and dyes due to its ability to dissolve a wide range of substances.
3. *Plasticizers*:
– TEG is used as a plasticizer in the production of polyurethanes and other polymers.
4. *Humectants*:
– TEG is used in personal care products like lotions, creams, and toothpaste to retain moisture.
5. *Heat Transfer Fluids*:
– TEG is used in heat transfer systems due to its high boiling point and thermal stability.
6. *Other Applications*:
– Used in the production of adhesives, paper, and textiles.
– Acts as a chemical intermediate in the synthesis of other compounds.
*Advantages of TEG:*
1. *Versatility*: Used in a wide range of industries.
2. *Efficiency*: Effective at low concentrations in applications like gas dehydration.
3. *Cost-Effective*: Relatively inexpensive compared to alternative chemicals.
*Disadvantages of TEG:*
1. *Toxicity*: Requires careful handling and storage.
2. *Environmental Concerns*: Improper disposal can harm ecosystems.
3. *Flammability*: Combustible at high temperatures.

Tehran, Saadat Abad, Keshavarz Boulevard, Sefid Tower
info@petrodmo.com
(+98) 990 312 4793
(+98) 991 108 8952
(+98) 912 833 4643
Copyright © 2025 PetroDMO